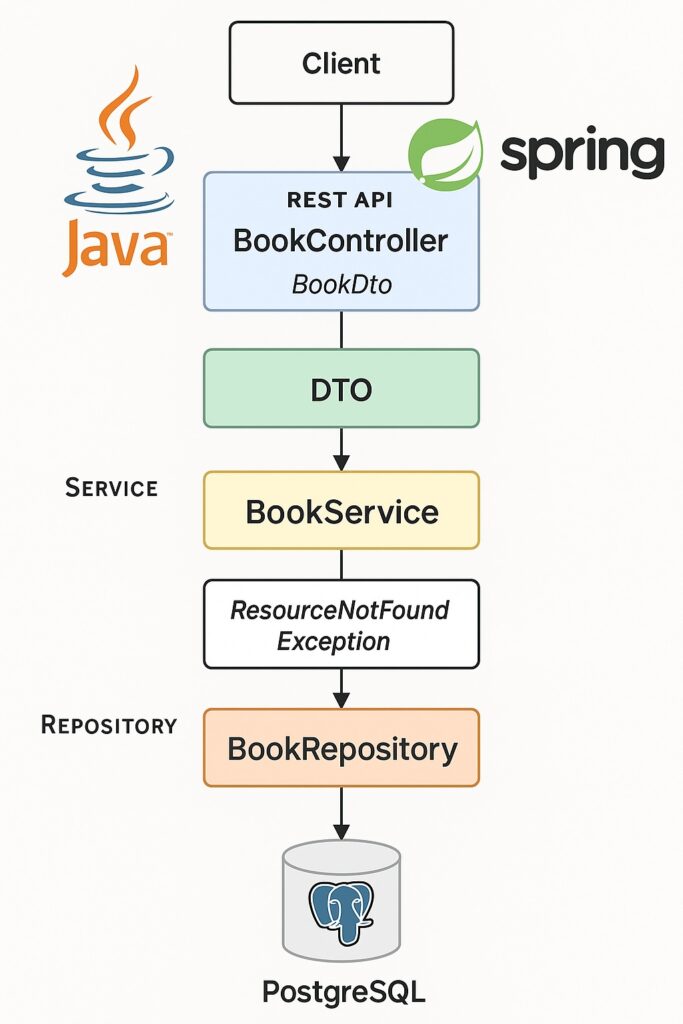
Developing RESTful APIs is a cornerstone of modern backend development. When using Java, Spring Boot is the go-to framework for quickly building robust and scalable APIs. Coupled with PostgreSQL, you get a powerful combination for handling data reliably.
In this article, you’ll learn:
- The best practices for building REST APIs with Spring Boot
- How to structure a Spring Boot project
- How to connect to PostgreSQL
- A full working example (CRUD API for a
Bookentity)
Best Practices Overview
Before diving into code, let’s establish some best practices:
| Area | Best Practice |
|---|---|
| Project Structure | Follow a layered architecture (Controller → Service → Repository) |
| DTO Usage | Use DTOs to separate internal models from API contracts |
| Validation | Use javax.validation annotations for request validation |
| Exception Handling | Use @ControllerAdvice to handle errors globally |
| Database Access | Use Spring Data JPA with proper pagination and sorting |
| Security | Secure endpoints with authentication (out of scope for this example) |
| Documentation | Use Swagger/OpenAPI for documentation |
Project Setup
Tools Used
- Java 17
- Spring Boot 3.x
- PostgreSQL
- Maven
- IntelliJ
Dependencies (in pom.xml)
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.postgresql</groupId>
<artifactId>postgresql</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-validation</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springdoc</groupId>
<artifactId>springdoc-openapi-starter-webmvc-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.0.2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>Project Structure
src/main/java/com/example/bookapi
├── controller
│ └── BookController.java
├── dto
│ └── BookDto.java
├── entity
│ └── Book.java
├── exception
│ ├── GlobalExceptionHandler.java
│ └── ResourceNotFoundException.java
├── repository
│ └── BookRepository.java
├── service
│ └── BookService.java
├── BookApiApplication.javaapplication.yml (or application.properties)
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/bookdb
username: postgres
password: yourpassword
jpa:
hibernate:
ddl-auto: update
show-sql: true
properties:
hibernate:
dialect: org.hibernate.dialect.PostgreSQLDialectEntity
// entity/Book.java
package com.example.bookapi.entity;
import jakarta.persistence.*;
import lombok.*;
@Entity
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Builder
public class Book {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String title;
private String author;
}DTO
// dto/BookDto.java
package com.example.bookapi.dto;
import jakarta.validation.constraints.NotBlank;
import lombok.*;
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Builder
public class BookDto {
private Long id;
@NotBlank(message = "Title is required")
private String title;
@NotBlank(message = "Author is required")
private String author;
}Repository
// repository/BookRepository.java
package com.example.bookapi.repository;
import com.example.bookapi.entity.Book;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
public interface BookRepository extends JpaRepository<Book, Long> {}Service Layer
// service/BookService.java
package com.example.bookapi.service;
import com.example.bookapi.dto.BookDto;
import com.example.bookapi.entity.Book;
import com.example.bookapi.exception.ResourceNotFoundException;
import com.example.bookapi.repository.BookRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
@Service
public class BookService {
@Autowired
private BookRepository bookRepository;
public BookDto createBook(BookDto dto) {
Book book = Book.builder()
.title(dto.getTitle())
.author(dto.getAuthor())
.build();
return toDto(bookRepository.save(book));
}
public List<BookDto> getAllBooks() {
return bookRepository.findAll().stream().map(this::toDto).toList();
}
public BookDto getBookById(Long id) {
Book book = bookRepository.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(() -> new ResourceNotFoundException("Book not found with id " + id));
return toDto(book);
}
public BookDto updateBook(Long id, BookDto dto) {
Book book = bookRepository.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(() -> new ResourceNotFoundException("Book not found"));
book.setTitle(dto.getTitle());
book.setAuthor(dto.getAuthor());
return toDto(bookRepository.save(book));
}
public void deleteBook(Long id) {
Book book = bookRepository.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(() -> new ResourceNotFoundException("Book not found"));
bookRepository.delete(book);
}
private BookDto toDto(Book book) {
return BookDto.builder()
.id(book.getId())
.title(book.getTitle())
.author(book.getAuthor())
.build();
}
}Controller
// controller/BookController.java
package com.example.bookapi.controller;
import com.example.bookapi.dto.BookDto;
import com.example.bookapi.service.BookService;
import jakarta.validation.Valid;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/books")
public class BookController {
@Autowired
private BookService bookService;
@PostMapping
public BookDto createBook(@RequestBody @Valid BookDto dto) {
return bookService.createBook(dto);
}
@GetMapping
public List<BookDto> getAllBooks() {
return bookService.getAllBooks();
}
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public BookDto getBook(@PathVariable Long id) {
return bookService.getBookById(id);
}
@PutMapping("/{id}")
public BookDto updateBook(@PathVariable Long id, @RequestBody @Valid BookDto dto) {
return bookService.updateBook(id, dto);
}
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
public void deleteBook(@PathVariable Long id) {
bookService.deleteBook(id);
}
}Global Exception Handler
// exception/ResourceNotFoundException.java
package com.example.bookapi.exception;
public class ResourceNotFoundException extends RuntimeException {
public ResourceNotFoundException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}// exception/GlobalExceptionHandler.java
package com.example.bookapi.exception;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.MethodArgumentNotValidException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(ResourceNotFoundException.class)
public ResponseEntity<?> handleNotFound(ResourceNotFoundException ex) {
return new ResponseEntity<>(Map.of("error", ex.getMessage()), HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
}
@ExceptionHandler(MethodArgumentNotValidException.class)
public ResponseEntity<?> handleValidation(MethodArgumentNotValidException ex) {
Map<String, String> errors = new HashMap<>();
ex.getBindingResult().getFieldErrors().forEach(e -> errors.put(e.getField(), e.getDefaultMessage()));
return new ResponseEntity<>(errors, HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST);
}
}Test with Swagger
Once the application is running, navigate to:
http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.htmlYou’ll see an interactive Swagger UI to test all endpoints.
Summary
You’ve built a production-ready, well-structured REST API using Java, Spring Boot, and PostgreSQL with best practices:
Layered architecture
DTO and validation
Exception handling
Swagger documentation
Clean code with Lombok and JPA