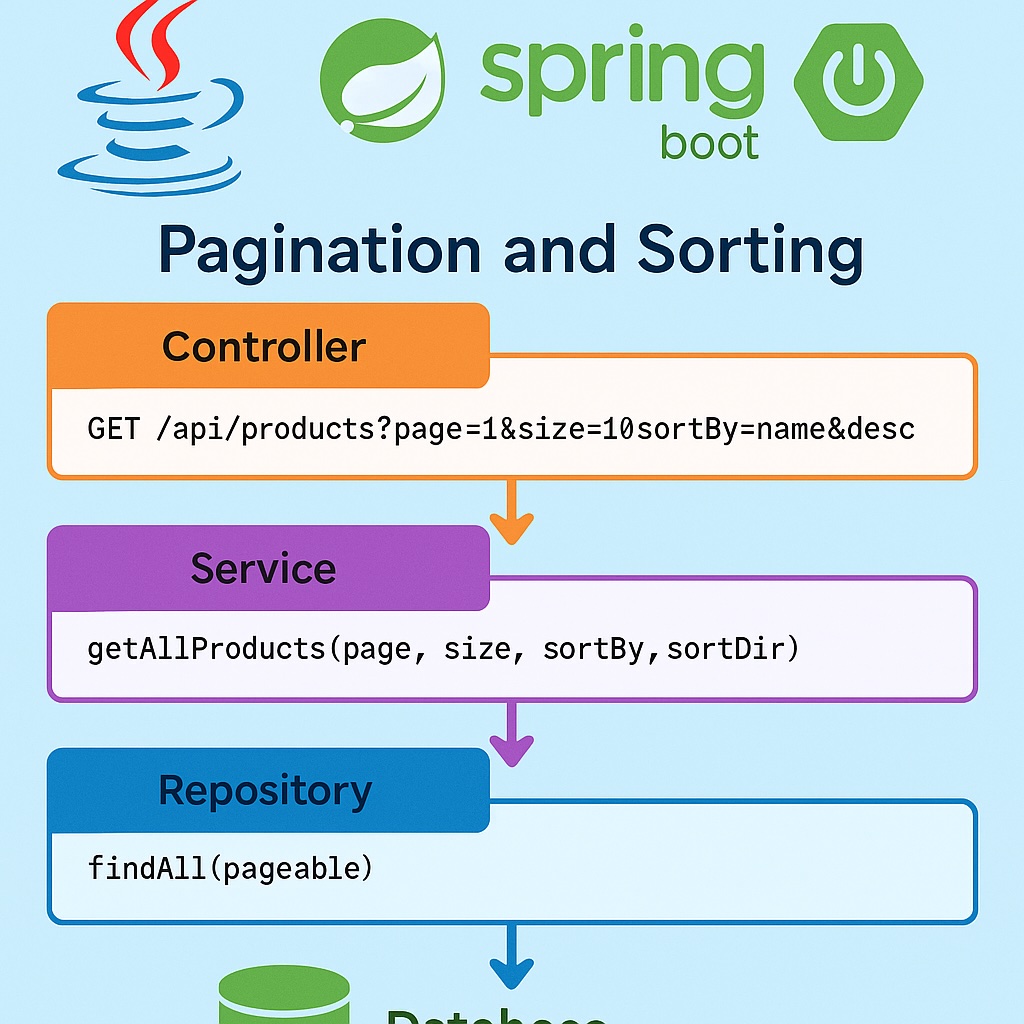
In modern web applications, handling large datasets efficiently is essential. Instead of returning all records at once (which is inefficient and memory-intensive), pagination and sorting help return manageable chunks of data, optionally sorted by any field.
Spring Data JPA provides built-in support for both pagination and sorting, allowing developers to implement them with minimal effort.
Technologies Used
- Java 17+
- Spring Boot 3.x
- Spring Data JPA
- H2 (In-memory database for demo)
- Maven
Project Setup
Add the following dependencies to your pom.xml:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>Entity Class
@Entity
public class Product {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String name;
private Double price;
// Constructors, Getters and Setters
}Repository Interface
Spring Data JPA provides the PagingAndSortingRepository and JpaRepository interfaces that support pagination and sorting.
public interface ProductRepository extends JpaRepository<Product, Long> {
}Service Layer
@Service
public class ProductService {
@Autowired
private ProductRepository productRepository;
public Page<Product> getAllProducts(int page, int size, String sortBy, String sortDir) {
Sort sort = sortDir.equalsIgnoreCase(Sort.Direction.ASC.name()) ?
Sort.by(sortBy).ascending() : Sort.by(sortBy).descending();
Pageable pageable = PageRequest.of(page, size, sort);
return productRepository.findAll(pageable);
}
}Controller Layer
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/products")
public class ProductController {
@Autowired
private ProductService productService;
@GetMapping
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> getProducts(
@RequestParam(defaultValue = "0") int page,
@RequestParam(defaultValue = "5") int size,
@RequestParam(defaultValue = "id") String sortBy,
@RequestParam(defaultValue = "asc") String sortDir) {
Page<Product> pageProducts = productService.getAllProducts(page, size, sortBy, sortDir);
Map<String, Object> response = new HashMap<>();
response.put("products", pageProducts.getContent());
response.put("currentPage", pageProducts.getNumber());
response.put("totalItems", pageProducts.getTotalElements());
response.put("totalPages", pageProducts.getTotalPages());
return new ResponseEntity<>(response, HttpStatus.OK);
}
}application.properties
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:testdb
spring.datasource.driverClassName=org.h2.Driver
spring.datasource.username=sa
spring.datasource.password=
spring.jpa.database-platform=org.hibernate.dialect.H2Dialect
spring.h2.console.enabled=true
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=createData Initialization
@Component
public class DataInitializer implements CommandLineRunner {
@Autowired
private ProductRepository productRepository;
@Override
public void run(String... args) {
for (int i = 1; i <= 50; i++) {
Product p = new Product();
p.setName("Product " + i);
p.setPrice(10.0 + i);
productRepository.save(p);
}
}
}Sample API Request
GET /api/products?page=1&size=10&sortBy=name&sortDir=desc
Response:
{
"products": [
{ "id": 49, "name": "Product 49", "price": 59.0 },
...
],
"currentPage": 1,
"totalItems": 50,
"totalPages": 5
}Summary
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Pagination | Achieved using PageRequest.of(page, size) |
| Sorting | Sort.by(field).ascending() or .descending() |
| Combined | Use PageRequest.of(page, size, sort) |
| Return Object | Page<T> with metadata: content, total pages, total items |
Best Practices
- Validate
page,size, andsortByinputs. - Default values prevent API errors.
- Avoid exposing entity classes directly (use DTOs in production).
- For complex filtering, consider using
Specificationor QueryDSL.